
Recycler用来实现对象池,其中对应堆内存和直接内存的池化实现分别是PooledHeapByteBuf和PooledDirectByteBuf。Recycler主要提供了3个方法:
- get():获取一个对象。
- recycle(T, Handle):回收一个对象,T为对象泛型。
- newObject(Handle):当没有可用对象时创建对象的实现方法。
Recycler的UML图如下:
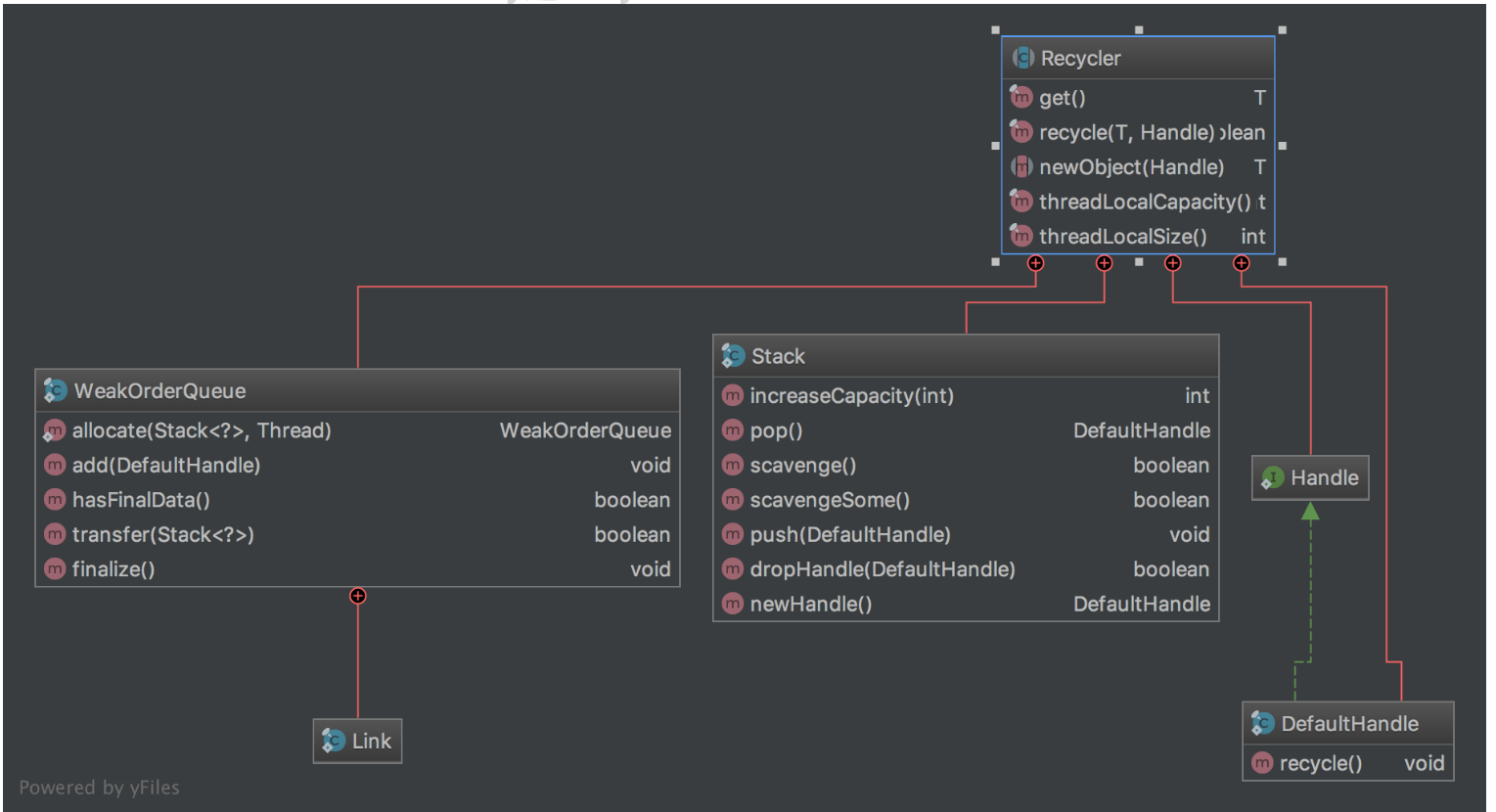
Recycler关联了4个核心类:
- DefaultHandle:对象的包装类,在Recycler中缓存的对象都会包装成DefaultHandle类。
- Stack:存储本线程回收的对象。对象的获取和回收对应Stack的pop和push,即获取对象时从Stack中pop出1个DefaultHandle,回收对象时将对象包装成DefaultHandle push到Stack中。Stack会与线程绑定,即每个用到Recycler的线程都会拥有1个Stack,在该线程中获取对象都是在该线程的Stack中pop出一个可用对象。
- WeakOrderQueue:存储其它线程回收到本线程stack的对象,当某个线程从Stack中获取不到对象时会从WeakOrderQueue中获取对象。每个线程的Stack拥有1个WeakOrderQueue链表,链表每个节点对应1个其它线程的WeakOrderQueue,其它线程回收到该Stack的对象就存储在这个WeakOrderQueue里。
- Link: WeakOrderQueue中包含1个Link链表,回收对象存储在链表某个Link节点里,当Link节点存储的回收对象满了时会新建1个Link放在Link链表尾。
整个Recycler回收对象存储结构如下图所示:
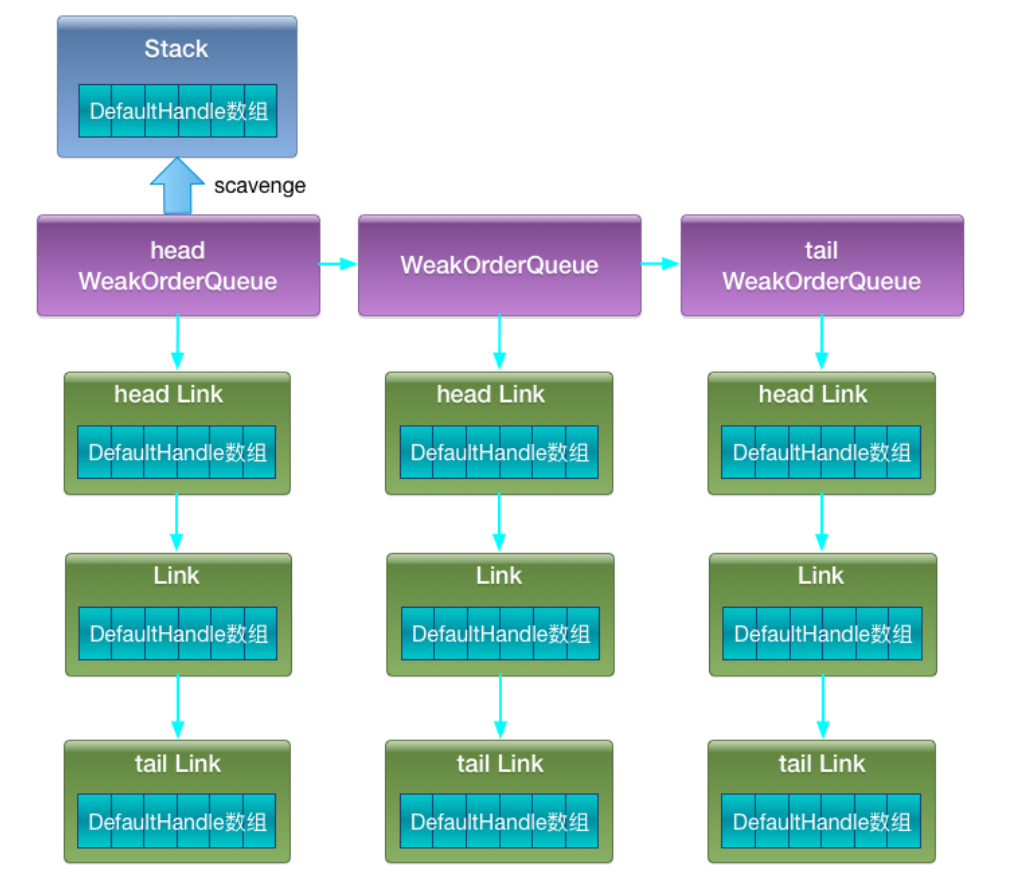
下面分析下源码,首先看下Recycler.recycle(T, Handle)方法,用于回收1个对象:
public final boolean recycle(T o, Handle handle) { if (handle == NOOP_HANDLE) { return false; } DefaultHandle h = (DefaultHandle) handle; if (h.stack.parent != this) { return false; } if (o != h.value) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("o does not belong to handle"); } h.recycle(); return true;} 回收1个对象会调用该对象DefaultHandle.recycle()方法,如下:
public void recycle() { stack.push(this); } 回收1个对象(DefaultHandle)就是把该对象push到stack中。
void push(DefaultHandle item) { Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread(); if (thread == currentThread) { // The current Thread is the thread that belongs to the Stack, we can try to push the object now. /** * 如果该stack就是本线程的stack,那么直接把DefaultHandle放到该stack的数组里 */ pushNow(item); } else { // The current Thread is not the one that belongs to the Stack, we need to signal that the push // happens later. /** * 如果该stack不是本线程的stack,那么把该DefaultHandle放到该stack的WeakOrderQueue中 */ pushLater(item, currentThread); } } 这里分为两种情况,当stack是当前线程对应的stack时,执行pushNow(item)方法,直接把对象放到该stack的DefaultHandle数组中,如下:
/** * 直接把DefaultHandle放到stack的数组里,如果数组满了那么扩展该数组为当前2倍大小 * @param item */ private void pushNow(DefaultHandle item) { if ((item.recycleId | item.lastRecycledId) != 0) { throw new IllegalStateException("recycled already"); } item.recycleId = item.lastRecycledId = OWN_THREAD_ID; int size = this.size; if (size >= maxCapacity || dropHandle(item)) { // Hit the maximum capacity or should drop - drop the possibly youngest object. return; } if (size == elements.length) { elements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, min(size << 1, maxCapacity)); } elements[size] = item; this.size = size + 1; } 当stack是其它线程的stack时,执行pushLater(item, currentThread)方法,将对象放到WeakOrderQueue中,如下:
private void pushLater(DefaultHandle item, Thread thread) { /** * Recycler有1个stack->WeakOrderQueue映射,每个stack会映射到1个WeakOrderQueue,这个WeakOrderQueue是该stack关联的其它线程WeakOrderQueue链表的head WeakOrderQueue。 * 当其它线程回收对象到该stack时会创建1个WeakOrderQueue中并加到stack的WeakOrderQueue链表中。 */ Map , WeakOrderQueue> delayedRecycled = DELAYED_RECYCLED.get(); WeakOrderQueue queue = delayedRecycled.get(this); if (queue == null) { /** * 如果delayedRecycled满了那么将1个伪造的WeakOrderQueue(DUMMY)放到delayedRecycled中,并丢弃该对象(DefaultHandle) */ if (delayedRecycled.size() >= maxDelayedQueues) { // Add a dummy queue so we know we should drop the object delayedRecycled.put(this, WeakOrderQueue.DUMMY); return; } // Check if we already reached the maximum number of delayed queues and if we can allocate at all. /** * 创建1个WeakOrderQueue */ if ((queue = WeakOrderQueue.allocate(this, thread)) == null) { // drop object return; } delayedRecycled.put(this, queue); } else if (queue == WeakOrderQueue.DUMMY) { // drop object return; } /** * 将对象放入到该stack对应的WeakOrderQueue中 */ queue.add(item); }static WeakOrderQueue allocate(Stack stack, Thread thread) { // We allocated a Link so reserve the space /** * 如果该stack的可用共享空间还能再容下1个WeakOrderQueue,那么创建1个WeakOrderQueue,否则返回null */ return reserveSpace(stack.availableSharedCapacity, LINK_CAPACITY) ? new WeakOrderQueue(stack, thread) : null; } WeakOrderQueue的构造函数如下,WeakOrderQueue实现了多线程环境下回收对象的机制,当由其它线程回收对象到stack时会为该stack创建1个WeakOrderQueue,这些由其它线程创建的WeakOrderQueue会在该stack中按链表形式串联起来,每次创建1个WeakOrderQueue会把该WeakOrderQueue作为该stack的head WeakOrderQueue:
private WeakOrderQueue(Stack stack, Thread thread) { head = tail = new Link(); owner = new WeakReference (thread); /** * 每次创建WeakOrderQueue时会更新WeakOrderQueue所属的stack的head为当前WeakOrderQueue, 当前WeakOrderQueue的next为stack的之前head, * 这样把该stack的WeakOrderQueue通过链表串起来了,当下次stack中没有可用对象需要从WeakOrderQueue中转移对象时从WeakOrderQueue链表的head进行scavenge转移到stack的对DefaultHandle数组。 */ synchronized (stack) { next = stack.head; stack.head = this; } availableSharedCapacity = stack.availableSharedCapacity; } 下面再看Recycler.get()方法:
public final T get() { if (maxCapacity == 0) { return newObject(NOOP_HANDLE); } Stack stack = threadLocal.get(); DefaultHandle handle = stack.pop(); if (handle == null) { handle = stack.newHandle(); handle.value = newObject(handle); } return (T) handle.value;} 取出该线程对应的stack,从stack中pop出1个DefaultHandle,返回该DefaultHandle的真正对象。
下面看stack.pop()方法:DefaultHandle pop() { int size = this.size; if (size == 0) { if (!scavenge()) { return null; } size = this.size; } size --; DefaultHandle ret = elements[size]; elements[size] = null; if (ret.lastRecycledId != ret.recycleId) { throw new IllegalStateException("recycled multiple times"); } ret.recycleId = 0; ret.lastRecycledId = 0; this.size = size; return ret; } 如果该stack的DefaultHandle数组中还有对象可用,那么从该DefaultHandle数组中取出1个可用对象返回,如果该DefaultHandle数组没有可用的对象了,那么执行scavenge()方法,将head WeakOrderQueue中的head Link中的DefaultHandle数组转移到stack的DefaultHandle数组,scavenge方法如下:
boolean scavenge() { // continue an existing scavenge, if any if (scavengeSome()) { return true; } // reset our scavenge cursor prev = null; cursor = head; return false; } 具体执行了scavengeSome()方法,清理WeakOrderQueue中部分DefaultHandle到stack,每次尽可能清理head WeakOrderQueue的head Link的全部DefaultHandle,如下:
boolean scavengeSome() { WeakOrderQueue cursor = this.cursor; if (cursor == null) { cursor = head; if (cursor == null) { return false; } } boolean success = false; WeakOrderQueue prev = this.prev; do { /** * 将当前WeakOrderQueue的head Link的DefaultHandle数组转移到stack的DefaultHandle数组中 */ if (cursor.transfer(this)) { success = true; break; } WeakOrderQueue next = cursor.next; if (cursor.owner.get() == null) { if (cursor.hasFinalData()) { for (;;) { if (cursor.transfer(this)) { success = true; } else { break; } } } if (prev != null) { prev.next = next; } } else { prev = cursor; } cursor = next; } while (cursor != null && !success); this.prev = prev; this.cursor = cursor; return success; } WeakOrderQueue.transfer()方法如下,将WeakOrderQueue的head Link中的DefaultHandle数组迁移到stack中:
boolean transfer(Stack dst) { Link head = this.head; if (head == null) { return false; } /** * 如果head Link的readIndex到达了Link的容量LINK_CAPACITY,说明该Link已经被scavengge完了。 * 这时需要把下一个Link作为新的head Link。 */ if (head.readIndex == LINK_CAPACITY) { if (head.next == null) { return false; } this.head = head = head.next; } final int srcStart = head.readIndex; /** * head Link的回收对象数组的最大位置 */ int srcEnd = head.get(); /** * head Link可以scavenge的DefaultHandle的数量 */ final int srcSize = srcEnd - srcStart; if (srcSize == 0) { return false; } final int dstSize = dst.size; /** * 每次会尽可能scavenge整个head Link,如果head Link的DefaultHandle数组能全部迁移到stack中,stack的DefaultHandle数组预期容量 */ final int expectedCapacity = dstSize + srcSize; /** * 如果预期容量大于stack的DefaultHandle数组最大长度,说明本次无法将head Link的DefaultHandle数组全部迁移到stack中 */ if (expectedCapacity > dst.elements.length) { final int actualCapacity = dst.increaseCapacity(expectedCapacity); srcEnd = min(srcStart + actualCapacity - dstSize, srcEnd); } if (srcStart != srcEnd) { /** * head Link的DefaultHandle数组 */ final DefaultHandle[] srcElems = head.elements; /** * stack的DefaultHandle数组 */ final DefaultHandle[] dstElems = dst.elements; int newDstSize = dstSize; /** * 迁移head Link的DefaultHandle数组到stack的DefaultHandle数组 */ for (int i = srcStart; i < srcEnd; i++) { DefaultHandle element = srcElems[i]; if (element.recycleId == 0) { element.recycleId = element.lastRecycledId; } else if (element.recycleId != element.lastRecycledId) { throw new IllegalStateException("recycled already"); } srcElems[i] = null; if (dst.dropHandle(element)) { // Drop the object. continue; } element.stack = dst; dstElems[newDstSize ++] = element; } /** * 当head节点的对象全都转移给stack后,取head下一个节点作为head,下次转移的时候再从新的head转移回收的对象 */ if (srcEnd == LINK_CAPACITY && head.next != null) { // Add capacity back as the Link is GCed. reclaimSpace(LINK_CAPACITY); this.head = head.next; } /** * 迁移完成后更新原始head Link的readIndex */ head.readIndex = srcEnd; if (dst.size == newDstSize) { return false; } dst.size = newDstSize; return true; } else { // The destination stack is full already. return false; } }